Blue skies innovation
Basic research (or blue skies research) may be defined as research to understand the basic mechanisms of nature. Such research is often regarded as curiosity driven and defined by scientists.
In sharper focus
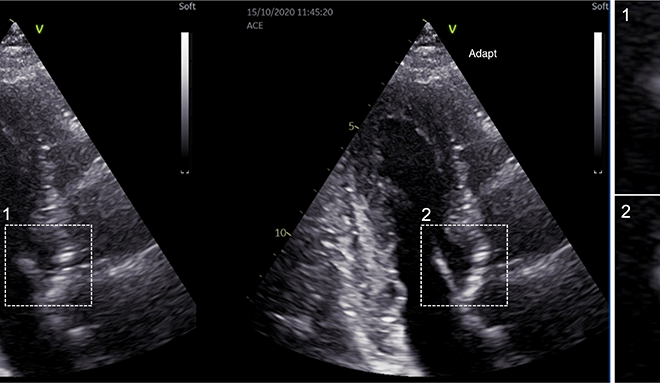
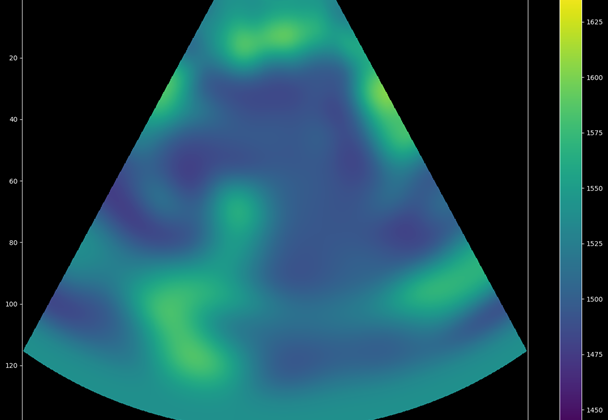
Take a 40-year-old problem of ‘unfocused’ ultrasound images, add dedicated researchers at a centre for research-based innovation, and the result? Sharper, clearer images regardless of the patient’s anatomy – a vitally important improvement for diagnosing heart attacks and their severity.
Higher resolution with new ultrasound probe design
Commercial ultrasound probe designs have their pros and cons, but what if we combine the pros of two designs to create a new type of transducer? One that can acquire more information and producer higher resolution images for improved cardiovascular diagnosis?
Crack-detecting waves
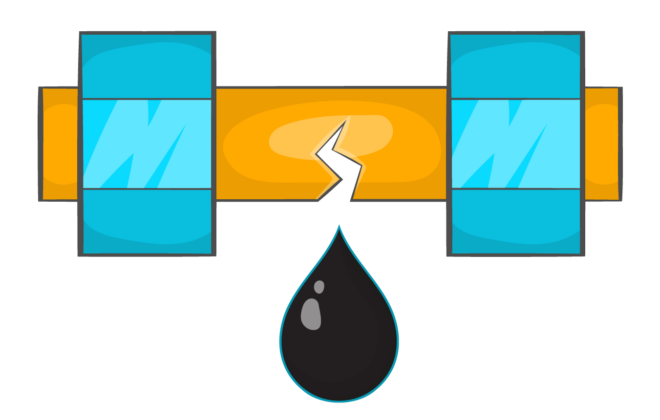
Whether they transport oil, gas, water, or other substances – you do not want them to leak. But if a pipe is in an inaccessible area, how do you then check for cracks? And if there are any – are they critical, or not?
Real-time project and real-life experience
When building a house, it is crucial to know whether the ground consists of rock, gravel, sand, or clay. The same goes for underwater installations, but it is not so easy to determine as on dry land.
Improving ultrasound imaging of obese patients
In 2016, over 1.9 billion adults were overweight, with more than 650 million classified as obese. In addition to the health risks these patients face, they have the additional problem of being difficult to image using ultrasound, which means doctors have to use more invasive, and often more expensive, imaging modalities.
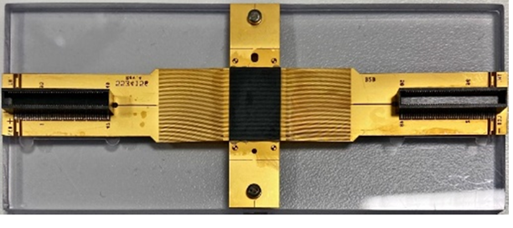
The heat is on – transducer design
To inspect and test oil pipelines is crucial – both for health and safety, and for the environment. But the harsh conditions mean specialised equipment is imperative. When using ultrasound to perform non-destructive testing, this translates into a need for transducers that can withstand extremely high temperatures.
Detecting the smallest leakages without delay
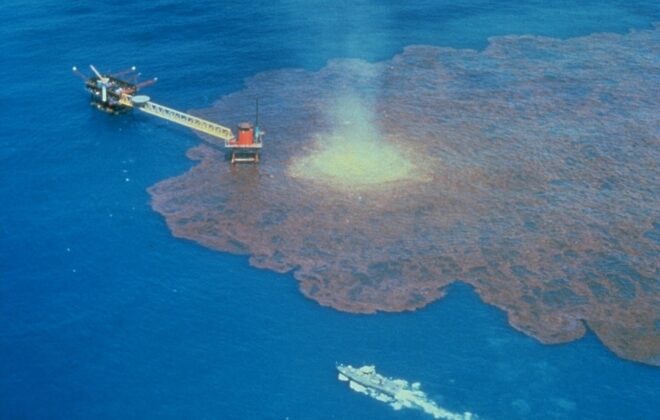
Leaks in oil & gas boreholes can have serious consequences. But current monitoring methods have a significant information delay and are not very sensitive. This is why we have developed a new method that eliminates delay, and which can detect the smallest leakages.
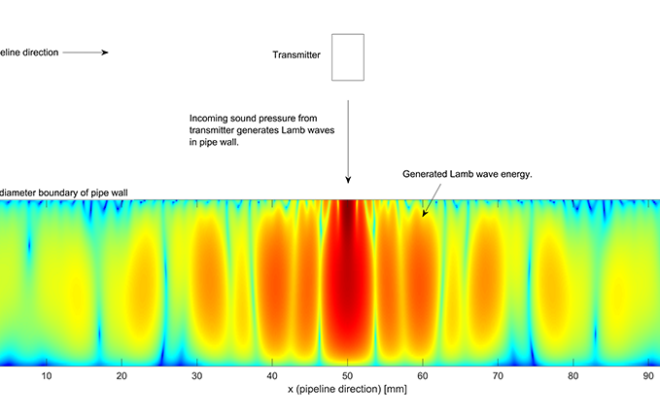
Ultrasound for improved crack detection
I have a created a modelling tool that can calculate ultrasonic sensitivity of cracks in pipelines, which is 8 times faster than commercial software. The model can simulate the behaviour and characteristics of waves within a pipe wall which are generated when an ultrasonic transmitter is radiating sound towards the pipe wall. These internal waves will be distorted somehow when encountering a crack, so knowing how these waves behave is vital in optimizing sensitivity in crack detection applications.
We built an AI tool to help avoid environmental disasters
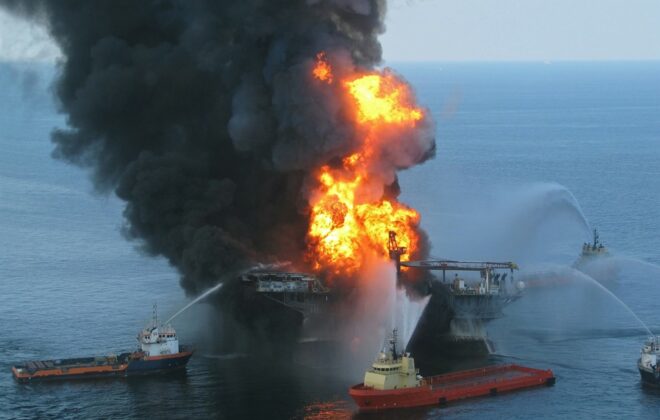
Artificial intelligence helps us more and more with decision-making in fields such as medicine, transportation, and information retrieval. In collaboration with Equinor, Norway’s biggest oil and gas company, we have now added another field to the list: Interpreting integrity logs from oil and gas wells. Together, we built an AI-based assistant for Equinor’s log interpreters that they are now using in their daily work.