Uncovering stiff or leaky heart valves
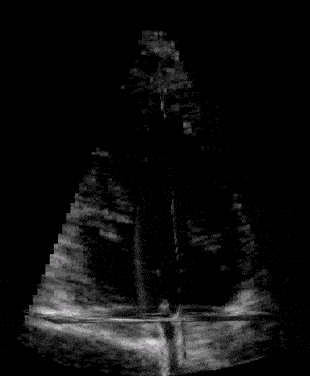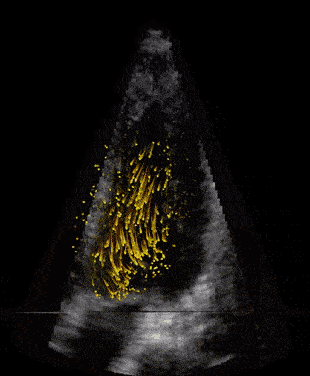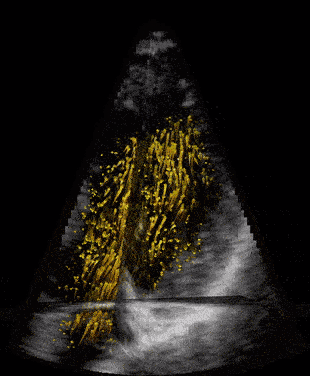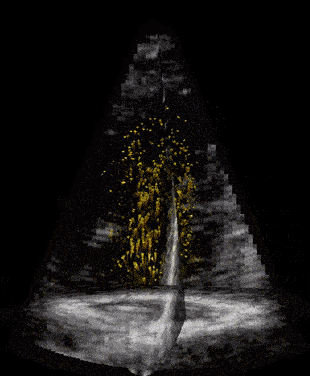
Modern ultrasound scanners combined with technological developments at NTNU may improve diagnostics for dis- eases related to narrow or leaky heart valves. Advanced 3D Doppler and high frame rate imaging makes it possible to visualise cardiac flow and minor movements of the heart’s muscular tissue more precisely, according to PhD Candidates Torvald Espeland and Erik Andreas Rye Berg.
Detecting issues in the foetal heart
How far can we get in detecting problems in the heart or vessels of the foetus during pregnancy? Using blood speckle tracking CIUS aims to detect problems in the heart and blood vessels of the unborn child with CIUS’ new partner, Austrian GE Healthcare Women’s Health Ultrasound (GEWHUS).
From meteorology to heart diagnostics
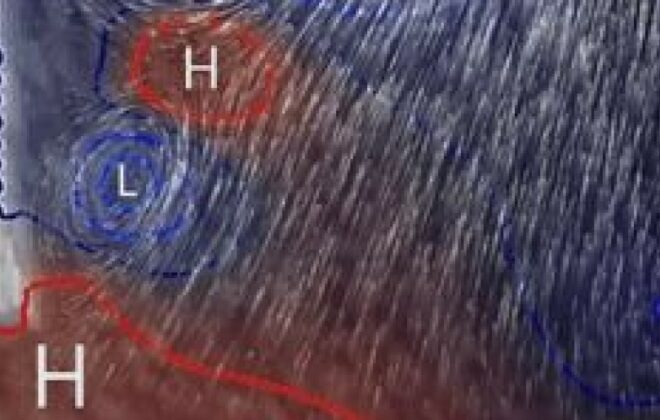
Weather forecasts have become a regular part of every day life, and much of the reliability behind these come from advanced techniques for combining weather observations with models based on physical principles. Using the same methods, we can help doctors discover heart disease at earlier…
The road to disputation
“I guess that was my last remark.” from the last challenger. 4.5 years summarized, questioned and discussed over three hours, and I was finally finished.
Assessing aortic stenosis severity by ultrasound
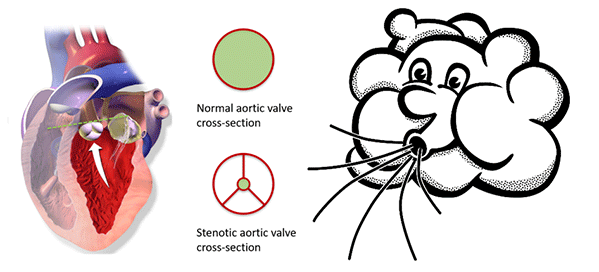
Aortic valve stenosis is a narrowing of the valve that separates the left ventricle from the aorta. A reduced opening increases the effort required by the left ventricle to pump blood. Being a degenerative disease, patients with aortic stenosis must undergo a clinical follow-up, which is usually performed by ultrasound. At the Centre of Innovative Ultrasound Solutions (CIUS), we are developing a new method that exploits 3-D high frame-rate imaging to increase the degree of automation in aortic stenosis flow measurements. The goal is to speed up the workflow in the clinics and increase the accuracy of measurements.
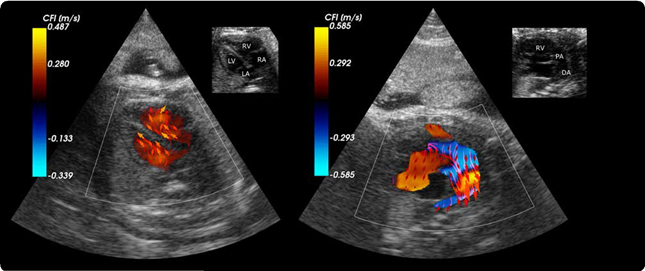
Measuring the heart’s blood flow behaviour in 3D
Given that cardiovascular related diseases are the most probable cause of death globally, according to WHO, we believe that more information regarding blood behaviour can help the doctors make better diagnosis at an earlier stage. But how can you measure these properties inside the heart, behind the ribs, under the skin, without moving the patients from their bed?
By Morten Smedsrud Wigen, PhD Candidate, Department of Circulation and Medical Imaging and CIUS – Centre for Innovative Ultrasound Solutions.
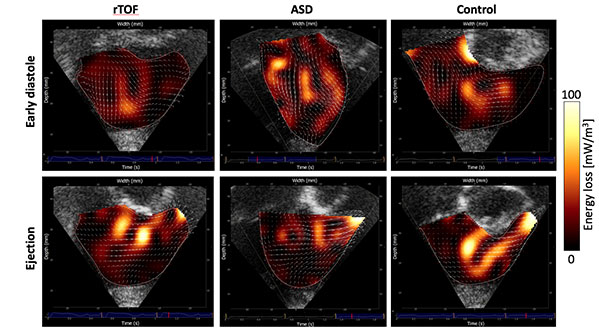
Blood flow secrets in small hearts
Using a new ultrasound technique, we have been able to visualize and measure how efficiently blood flows through the heart chambers in young children with congenital heart disease. We studied 37 children aged two weeks to 10 years, and among the 26 children, which had congenital heart disease, we found less efficient hearts, meaning they use more energy than a normal heart.