Department of Chemical Engineering
Annual Report 2015
9
NEW REACTOR CONCEPTS AND STRUCTURED
SUPPORTS
Emerging reactor technologies such as microstructured
reactors and (catalytic) membrane reactors are being
developed and tested.
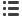
Examples of microstructured reactors
(Photo: Thor Nielsen)
PHOTOCATALYSIS
Accelerated environmental pollution on a global scale
has drawn attention to the need for totally new
environmentally
friendly
and
clean
chemical
technologies. The application of photocatalysis to reduce
toxic agents in air and water by developing catalysts that
can utilise clean and abundant solar energy and convert
it into useful chemical energy is a promising challenge.
Photocatalysts that can operate at ambient temperature
without producing harmful by-products are ideal as
environmentally sound catalysts. For such systems to be
considered in large-scale applications, photocatalytic
systems that are able to operate effectively and
efficiently using sunlight must be established. Hydrogen
can be produced by photoinduced reforming of organic
compounds,
including
methane
and
alcohols.
Furthermore, the photoreduction of carbon dioxide into
useful chemicals is a desirable prospect. It is essential to
convert CO
2
into useful substances that are common
feedstocks for the production of other chemicals (C
2
-C
3+
,
alcohols, etc.).
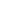
Photocatalytic reactor system.
CONVERSION OFLIGNOCELLULOSIC BIOMASS
TO CHEMICALS AND FUELS
The research isfocused on catalytic aspects of
thermochemical conversion, such as bio-oil upgrading,
syngas cleaning and composition adjustment, residual
hydrocarbon reforming and Fischer-Tropsch synthesis.
Due to the declining reserves and environmental effects
of fossil resources, a transition to renewable carbon
sources is important. Lignocellulosic biomass, such as
trees, is the most abundant biomass and one of the most
promising renewable carbon sources.
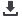
Conversion of biomass into useful chemicals
NATURAL GAS CONVERSION
Natural gas is an abundant hydrocarbon fuel and
chemical feedstock, and utilizing this resource with
minimum environmental impact is a major challenge to
catalysis. The main goal is to study catalytic processes for
conversion of natural gas to chemicals and fuels
including hydrogen. The work includes production of
synthesis
gas,
Fischer-Tropsch
synthesis,
and
dehydrogenation of C
2
-C
4
alkanes. The work is carried